数据库常见操作
增
删
改
查
条件
通配符
限制
排序
分组
连表操作
测试题
测试题
临时表
数据库常见操作
增
insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...)
insert into 表 (列名,列名...) values (值,值,值...),(值,值,值...)
insert into 表 (列名,列名...) select (列名,列名...) from 表
删
delete from 表
delete from 表 where id=1 and name='alex'
改
update 表 set name = 'alex'
update 表 set name = 'alex' where id>1
查
select * from 表
select * from 表 where id > 1
select nid,name,gender as gg from 表 where id > 1
条件
select * from 表 where id > 1 and name != 'alex' and num = 12;
select * from 表 where id between 5 and 16;
select * from 表 where id in (11,22,33)
select * from 表 where id not in (11,22,33)
select * from 表 where id in (select nid from 表)
通配符
select * from 表 where name like 'ale%' - ale开头的所有(多个字符串)
select * from 表 where name like 'ale_' - ale开头的所有(一个字符)
限制
select * from 表 limit 5; - 前5行
select * from 表 limit 4,5; - 从第4行开始的5行(取5个)
select * from 表 limit 5 offset 4 - 从第4行开始的5行
排序
select * from 表 order by 列 asc - 根据 “列” 从小到大排列
select * from 表 order by 列 desc - 根据 “列” 从大到小排列
select * from 表 order by 列1 desc,列2 asc - 根据 “列1” 从大到小排列,如果相同则按列2从小到大排序
分组
# 创建测试数据
mysql> create table department(id int auto_increment primary key,title varchar(32)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
mysql> insert into department(title) VALUES ('技术部'),('行政部'),('运营部'),('销售部')
mysql> create table userinfo(id int auto_increment primary key,name varchar(32),age int,part_id int,CONSTRAINT department_userinfo FOREIGN key (part_id) REFERENCES department(id)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
mysql> insert into userinfo(name,age,part_id) VALUES ('cce',18,1),('cfj',16,2),('csw',30,4),('cys',60,4),('dxf',30,3);
mysql> select * from department;
+----+--------+
| id | title |
+----+--------+
| 1 | 技术部 |
| 2 | 行政部 |
| 3 | 运营部 |
| 4 | 销售部 |
+----+--------+
mysql> select * from userinfo;
+----+------+------+---------+
| id | name | age | part_id |
+----+------+------+---------+
| 1 | cce | 18 | 1 |
| 2 | cfj | 16 | 2 |
| 3 | csw | 30 | 4 |
| 4 | cys | 60 | 4 |
| 5 | dxf | 30 | 3 |
+----+------+------+---------+
# 统计part_id出现的次数
mysql> select part_id,count(id) from userinfo group by part_id;
+---------+-----------+
| part_id | count(id) |
+---------+-----------+
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 1 |
| 3 | 1 |
| 4 | 2 |
+---------+-----------+
# 如果要对聚合函数进行二次筛选,那么就必须使用having
mysql> select part_id,count(*) from userinfo group by part_id having count(id) > 1;
+---------+----------+
| part_id | count(*) |
+---------+----------+
| 4 | 2 |
+---------+----------+
连表操作
语法:
select * from 表1 left join 表2 on 条件
select * from 表1 left join 表2 on 条件1 left join 表3 on 条件2
# 基本的连表操作
[cce]> select * from userinfo,department where userinfo.part_id=department.id;
# left是指左边表会全部显示
[cce]> select * from userinfo left join department on department.id=userinfo.part_id;
# right是指右边表会全部显示
[cce]>select * from userinfo right join department on userinfo.part_id=department.id;
# inner将出现NULL的一行隐藏
[cce]>select * from userinfo inner join department on userinfo.part_id=department.id;
测试题
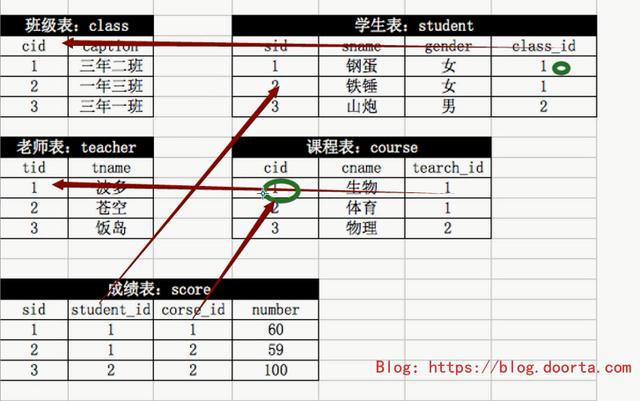
测试题
1、自行创建测试数据;
# class表结构
mysql> create table class(cid int auto_increment,caption char(32),primary key(cid)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
# teacher表结构
mysql> create table teacher(tid int auto_increment,tname char(32),primary key(tid)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
# student表结构
mysql> create table student(sid int auto_increment,sname char(32) not null, gender enum('男','女'),class_id int,primary key(sid),foreign key(class_id) references class(cid)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
# course表结构
mysql> create table course(cid int auto_increment,cname char(10) not null, teacher_id int,primary key(cid),foreign key(teacher_id) references teacher(tid))engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
# score表结构
mysql> create table score(sid int auto_increment,student_id int,course_id int,number int(10),primary key(sid),foreign key(student_id) references student(sid),foreign key(course_id) references course(cid),unique key(student_id,course_id)) engine=innodb default charset=utf8;
# 插入测试数据
mysql> insert into class(caption) values ('三年二班'),('一年三班'),('三年一班');
mysql> insert into teacher(tname) values ('波多'),('苍空'),('饭岛');
mysql> insert into student(sname,gender,class_id) values ('钢蛋','女',1),('铁锤','女',1),('山炮','男',2);
mysql> insert into course(cname,teacher_id) values ('生物',1),('体育',1),('物理',2);
mysql> insert into score(student_id,course_id,number) values (1,1,60),(1,2,59),(2,2,100);
临时表
mysql> select sid from (select * from score where number > 60) as B; # 将结果赋值给B
版权声明:本站所有资料均为网友推荐收集整理而来,仅供学习和研究交流使用。

工作时间:8:00-18:00
客服电话
电子邮件
admin@qq.com
扫码二维码
获取最新动态
