写在前面:
博客书写牢记5W1H法则:What,Why,When,Where,Who,How。
本篇主要内容:
● 权限认证
● SELinux运作模式/启动模式
● 安全上下文查看与修改
简介:
linux 安全软件、 SELinux全称为Security Enhanced Linux,意味安全强化linux。
其设计目的为防止“内部员工的资源误用”。是以进程、文件等细部权限设定为依据的一个核心模块。
360 linux。权限认证:
(1)传统文件权限与账号关系:自主式访问控制,DAC(Discretionary Access Control)
当某进程需要对文件进行存取操作时,系统会根据进程发起人对比文件权限,若通过权限检查,就可以存取文件。即依据进程拥有者与文件rwx权限来确定进程权限。
redis安全加固。 可能由于用户误操作导致资源误用,甚至对关键文件造成损害。如由于管理员为文件赋予了较宽泛权限,导致普通用户对关键文件有了修改权限等。
(2)针对特定进程与特定文件资源进行权限监控的规则:强制/委任式访问控制,MAC(Mandatory Access Control)
同一用户使用不同进程时,所获取到的权限不同。根据进程的权限设定确定权限,即将权限控制主体由用户变成了进程,以达到更加细化的控制权限的目的。
redis 高可用。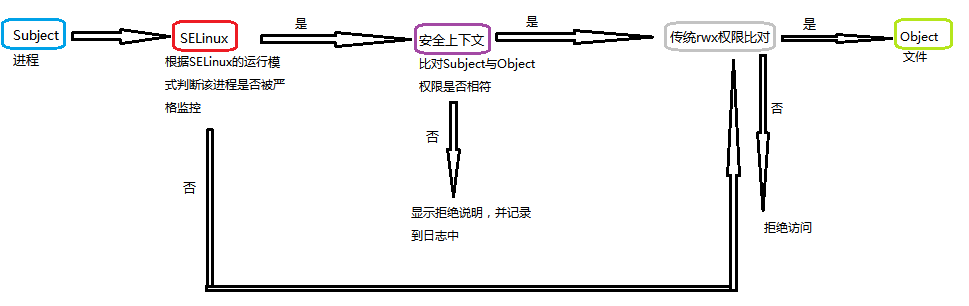
SELinux的运作模式:
Subject --Policy--> Object
SELINUX、 Subject:主体,即进程
Policy:预定策略,还可细分为详细的规则(rule),即预先定义的一系列布尔值集合。
相关配置文件:/etc/selinux/config
centOS6:
targeted:部分SELinux权限控制,仅严格监控网络服务的进程权限
strict:完全的SELinux权限控制,严格监控所有进程权限
centOS7:
targeted:部分SELinux权限控制,仅严格监控网络服务的进程权限
minimum:targeted修订而来,仅监控已选择的进程权限
mls:完全的SELinux权限控制,严格监控所有进程权限
Object:目标,即文件或其他进程
相关命令:
查看/修改SELinux规则是否启用。
getsebool
getsebool -a
获取SELinux布尔值规则列表
getsebool BOOLEAN
获取某个SELinux布尔值规则
setsebool
setsebool [-P] BOOLEAN VALUE | BOOLEAN1=VAL1 ...
修改布尔值,-P指定长期有效
例:
[root@localhost html]# getsebool -a | grep httpd allow_httpd_anon_write --> off allow_httpd_mod_auth_ntlm_winbind --> off allow_httpd_mod_auth_pam --> off allow_httpd_sys_script_anon_write --> off httpd_builtin_scripting --> on ...省略部分输出... [root@localhost html]# setsebool allow_httpd_anon_write on [root@localhost html]# getsebool allow_httpd_anon_write allow_httpd_anon_write --> on
安全上下文:(security context)
SELinux为每个文件提供了安全标签,同时也为进程提供了安全标签,这样通过比对进程与文件的安全标签,即可确定是否满足访问权限。
虽然条目中有3部分,但与进程能否访问文件资源有关的只有第3字段而已!当domain(进程的第3字段)与type(文件的第3字段)匹配时,就可以访问,与其他字段无关!
对不匹配安全标签的或没有明确规定有权限的操作一律拒绝。
安全标签存储位置:
进程:内存中
文件:inode
格式:
文件与进程的标签都为冒号隔开的3部分组成,但意义不尽相同:
文件:
Object:role:type
对象:角色:类型
进程:
Subject:role:domain
主题:角色:域
Object/Subject:
相当于传统权限中的用户。如:
unconfined_u:不受限用户,登陆用户进程或文件大多会被识别为这个
system_u:系统用户,系统或软件产生的进程或文件
role:
描述了此资源是进程、文件还是用户。
object_r:此资源为文件
unconfined_r:此资源为用户进程
system_r:此资源为系统进程
Type/domain:
只有domain匹配type时,进程才能够顺利读取文件资源。
安全上下文的查看:
文件:
ls -Z FILE
进程:
ps -eZ
SELinux启动模式:
enforcing:强制模式
permissive:宽容模式,仅警告(写入日志),不实际限制
disabled:关闭
相关配置文件:
/etc/selinux/config
相关命令:
getenforce
获取selinux当前启动模式
setenforce 0|1
设置selinux当前启动模式
0:enforcing
1:permissive
此种设定方法重启系统后失效。
修改安全上下文:
chron
chcon [OPTION]... CONTEXT FILE...
chcon [OPTION]... [-u USER] [-r ROLE] [-t TYPE] FILE...
chcon [OPTION]... --reference=RFILE FILE...
-R:递归打标
restorecon [-R] FILE
例:
#安装httpd服务 [root@localhost ~]# yum -y install httpd [root@localhost ~]# service httpd start Starting httpd: httpd: Could not reliably determine the server's fully qualified domain name, using localhost.localdomain for ServerName[ OK ] [root@localhost ~]# cd /var/www/html/ [root@localhost html]# echo "<h1>It works.</h1>" > index.html#浏览器访问http://IP,发现页面可以正常访问。#查看index.html文件权限及httpd进程权限 [root@localhost html]# ls -Z index.html -rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 index.html [root@localhost html]# ps auxZ | grep -v 'grep' | grep 'httpd' unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 root 5980 0.0 0.3 183856 3840 ? Ss 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5983 0.0 0.2 183856 2468 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5984 0.0 0.2 183856 2468 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5985 0.0 0.2 183856 2468 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5986 0.0 0.3 183992 3128 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5987 0.0 0.2 183856 2468 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5988 0.0 0.2 183856 2468 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5989 0.0 0.2 183856 2468 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd unconfined_u:system_r:httpd_t:s0 apache 5990 0.0 0.2 183856 2468 ? S 15:28 0:00 /usr/sbin/httpd↑↑ 可以看到进程domain为httpd_t,而文件type为httpd_sys_content_t,可以匹配,所以正确可访问#修改index.html安全上下文标签 [root@localhost html]# chcon -t admin_home_t index.html [root@localhost html]# ls -Z index.html -rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:admin_home_t:s0 index.html#浏览器访问http://IP,发现页面无法正确显示。#恢复初始安全上下文标签 [root@localhost html]# restorecon index.html [root@localhost html]# ls -Z index.html -rw-r--r--. root root unconfined_u:object_r:httpd_sys_content_t:s0 index.html↑↑ 页面访问恢复正常。
查看进程的domain能够读取那些文件的type,可以安装setools-console-*软件包并使用sesearch命令,详细查看鸟哥第4版基础篇P756。

![[vijos1162]波浪数](https://images.cnblogs.com/OutliningIndicators/ContractedBlock.gif)


![[转]Oracle修改监听口令](/upload/rand_pic/2-1144.jpg)